Music technology has undergone a remarkable transformation, evolving from the mechanical innovations of the 19th century to the sophisticated digital tools of today. This article explores this journey, highlighting key milestones that have shaped how we create, experience, and understand music.
An accompanying infographic provides a visual timeline, serving as an educational resource to illustrate these developments. You can utilize this infographic to foster discussions about the interplay between technology and music throughout history. To download and print the Music Tech Timeline poster, please subscribe below to receive a PDF version.

Subscribe now to instantly download Music Technology Historical Timeline Poster and unlock exclusive tools to enhance your music teaching!
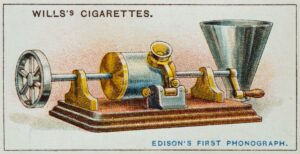
The Phonograph: Thomas Edison’s Groundbreaking Invention (1877)
In 1877, Thomas Edison introduced the phonograph, the first device capable of recording and reproducing sound. This invention marked the beginning of the acoustic era in sound recording, allowing for the capture and playback of audio.
The Pianola: Automated Music Playback (1896)
Edwin S. Votey completed the first Pianola, or player piano, in 1896. This instrument enabled automated music playback through perforated paper rolls, bringing music into homes without the need for a live performer.

The Telegraphone: Pioneering Magnetic Recording (1898)
Valdemar Poulsen patented the Telegraphone in 1898, introducing the concept of magnetic sound recording. This technology laid the groundwork for future developments in audio recording.

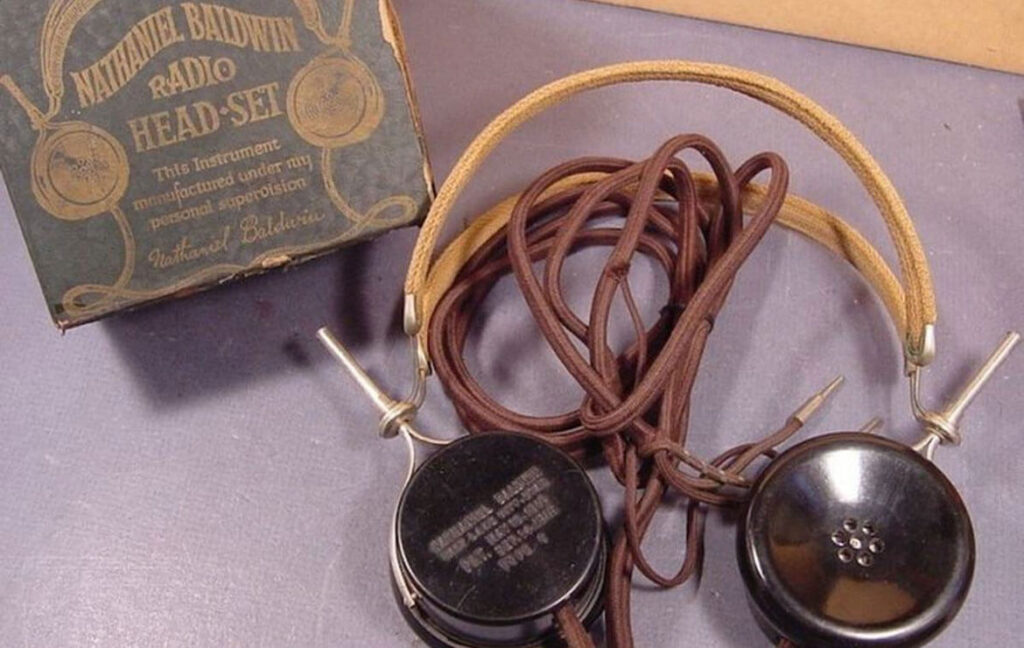
The First Headphones: Nathaniel Baldwin’s Innovation (1910)
In 1910, Nathaniel Baldwin constructed the first set of headphones using an operator’s headband and copper wire. Despite initial commercial challenges, the U.S. Navy recognized their potential and purchased hundreds in anticipation of possible world war.

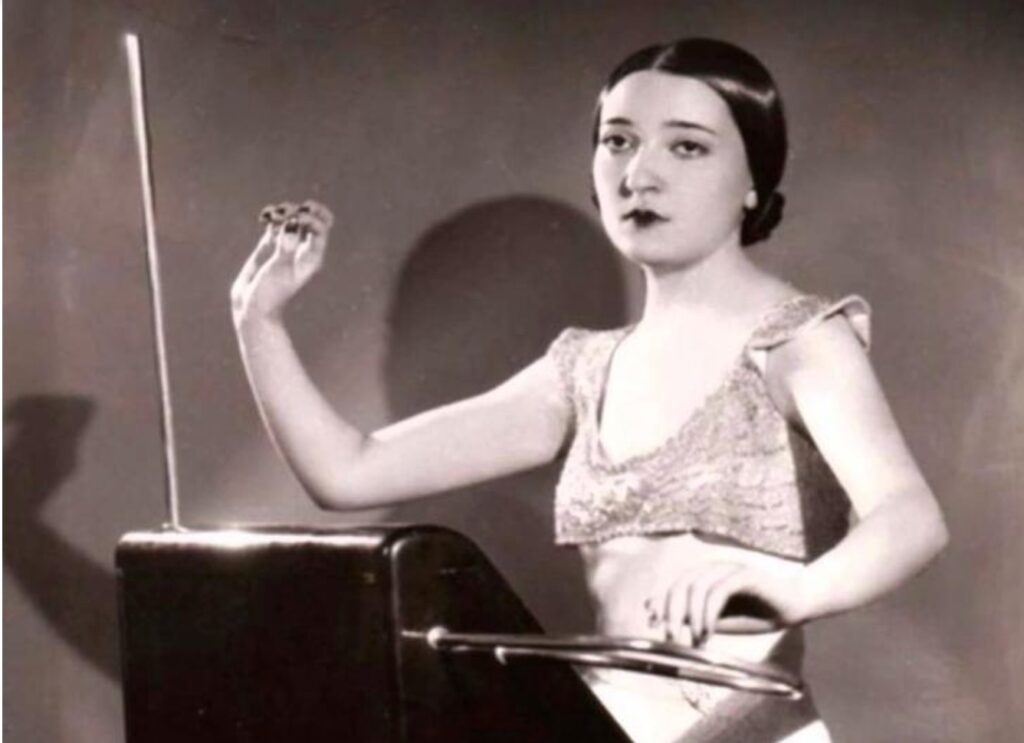
The Theremin: Touchless Musical Expression (1920)
Invented by Leon Theremin in 1920, the Theremin was one of the first electronic musical instruments, notable for being played without physical contact. It introduced a new form of musical expression and influenced future electronic instruments.

Subscribe now to instantly download Music Technology Historical Timeline Poster and unlock exclusive tools to enhance your music teaching!
Magnetic Tape Recording: Fritz Pfleumer’s Patent (1928)
Fritz Pfleumer patented a system for recording on paper coated with a magnetizable, powdered steel layer in 1928. This innovation was a precursor to magnetic tape recording, revolutionizing audio storage and playback.

Vinyl Record Player and the LP Format: RCA-Victor’s Innovation (1931)
In 1931, RCA-Victor began manufacturing 33⅓ RPM vinyl record players. Initially marketed as “Program Transcriptions,” they gained popularity post-1948 when Columbia Records reintroduced the format, leading to the widespread adoption of long-playing records.

The Hammond Organ: A New Sound in Music (1934)
Laurens Hammond created the first Hammond Organ in 1934, an electric organ that became popular in various music genres, including jazz and gospel.

The Ondioline: Georges Jenny’s Creation (1941)
Georges Jenny developed the Ondioline in 1941, an electronic keyboard instrument capable of producing a variety of sounds, contributing to the evolution of electronic music.

The Rhodes Piano: Harold Rhodes’ Prototype (1946)
Harold Rhodes built the first prototype of the Rhodes Piano in 1946, an electric piano that gained prominence in jazz and rock music for its distinctive sound.

Subscribe now to instantly download Music Technology Historical Timeline Poster and unlock exclusive tools to enhance your music teaching!
The Transistor and Microgroove Records: 1948 Milestones
Bell Laboratories unveiled the first transistor in 1948, revolutionizing electronic circuits. The same year, Columbia Records introduced the microgroove 33⅓ RPM vinyl record (LP), enhancing audio quality and playback duration.

The Pultec EQP-1 Equalizer: A Studio Staple (1951)
Pultec introduced the first passive program equalizer, the EQP-1, in 1951, which became a staple in audio recording and production for its ability to shape sound.

The RCA Synthesizer: Early Sound Synthesis (1952)
In 1952, Harry F. Olson and Herbert Belar invented the RCA Synthesizer, an early attempt at electronic sound synthesis that laid the groundwork for future synthesizers.

Integrated Circuits and Drum Machines: Late 1950s Innovations
Jack Kilby at Texas Instruments created the first integrated circuit in 1958, paving the way for modern electronics. In 1959, Wurlitzer manufactured The Sideman, the first commercial electro-mechanical drum machine, influencing rhythm composition in music.

The Compact Cassette: Philips’ Introduction (1963)
Philips introduced the Compact Cassette tape format in 1963, revolutionizing personal audio recording and playback with its portability and ease of use.

Subscribe now to instantly download Music Technology Historical Timeline Poster and unlock exclusive tools to enhance your music teaching!
The Moog Synthesizer: A New Era in Sound (1964)
Robert Moog released the Moog synthesizer in 1964, bringing electronic sound synthesis to mainstream music and influencing countless artists and genres.

Digital Audio and MIDI (1982)
Sony and Philips introduce the compact disc, offering digital audio playback. The same year, the first MIDI synthesizers are released, including the Roland Jupiter-6 and Prophet 600. In 1983, MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is officially unveiled, standardizing communication between electronic instruments.

The First DAW—Digital Audio Workstation (1989)
Digidesign released Sound Tools, a precursor to the industry-standard Pro Tools. This development marked a pivotal moment, as it combined digital recording with non-destructive editing capabilities, allowing for greater flexibility and precision in music production.
Throughout the 1990s and 2000s, several DAWs gained prominence:
- Cubase: Introduced by Steinberg, Cubase became renowned for its MIDI sequencing capabilities and later integrated audio recording features.
- Logic Pro: Initially developed by Emagic and later acquired by Apple, Logic Pro offered a comprehensive suite of tools for music composition and production.
- FL Studio: Known for its user-friendly interface and pattern-based music sequencing, FL Studio became a favorite among electronic music producers.
- Ableton Live: Praised for its real-time performance features, Ableton Live bridged the gap between studio production and live performances.
These platforms democratized music creation, making high-quality production accessible to a broader audience and fostering innovation across genres.

Artificial Intelligence in Music: The New Frontier
In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has begun to play a transformative role in music composition and production. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets of existing music to generate new compositions, assist in mixing and mastering, and even emulate the styles of specific artists.
Tools like AIVA (Artificial Intelligence Virtual Artist) allow users to create original compositions in various styles within seconds, serving as a source of inspiration and a collaborative partner in the creative process.
Moreover, AI has been utilized to complete unfinished works of renowned composers. For example, an AI program developed by Huawei assisted composer Lucas Cantor in finishing Schubert’s unfinished Symphony No. 8 by suggesting new melodies, which Cantor then curated and orchestrated.
While AI’s integration into music raises questions about creativity and authenticity, many artists view it as a tool that enhances human creativity rather than replacing it. By automating routine aspects of music production, AI allows musicians to focus more on the expressive and emotive elements of their work.

Subscribe now to instantly download Music Technology Historical Timeline Poster and unlock exclusive tools to enhance your music teaching!